Combining our efforts in moving the field forward
In recent decades, researchers in Aotearoa New Zealand, particularly the universities, have been carrying out fundamental research in AI, including in both of the high-level research streams of symbolic AI and subsymbolic/computational AI.
All of this fundamental AI research is vitally important as it provides the theoretical and algorithmic base that underpins and powers AI applications.
Some of the research, international collaborations and application strengths at our universities
[Use the left and right arrows down the side of the page to navigate through]
University of Otago
The University of Otago has strong and diverse expertise in AI and its implications. The University hosts the Centre for AI and Public Policy that includes researchers studying both the technical aspects and social implications of AI, and includes several researchers involved in the Global Partnership on AI's Responsible Use of AI working group. On the technical side, the School of Computing has researchers studying the fundamentals of AI including the theoretical foundations of neural networks, deep reinforcement learning, deep transfer learning, evolutionary computation and multi-agent systems as well as applications of AI to medical imaging, neurology, robotics, education and search. In addition, the Department of Mathematics and Statistics has significant expertise in Bayesian methods, which are the basis for many machine learning algorithms.
Auckland University of Technology
Researchers at Auckland University of Technology (AUT) are working on computational theories of the mind, methods and systems for computational intelligence, general game playing, AI in healthcare and medicine, multi-agent systems, recommender systems, human activity recognition, social network analysis, computer vision, natural language processing, robotics, and nature-inspired computing. AUT AI researchers collaborate with many international organisations, including Nanyang Technological University (Singapore), Warsaw University of Technology (Poland), Dublin Institute of Technology (Ireland), University of the Basque Country (Spain), Ecole Centrale de Nantes (France), Budapest University of Technology and Economics (Hungary), Griffith University (Australia), the University of New South Wales (Australia), Xinjiang University (China), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (China), Liverpool University (UK), Temple University Philadelphia (USA), King’s College Hospital (UK), Oregon Health and Science University (USA), Children’s Hospital of Fudan University (China), Beijing Institute of Life Sciences (China), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (China), Yale University (USA), Nottingham Trent University (UK), Deakin University (Australia), Macquarie University (Australia), Swinburne University of Technology (Australia), North China University of Technology (China), TU Wien (Austria), Shenzhen Technology University (China), Flinders University (Australia), University of Tasmania (Australia), Kyoto University (Japan), University of Technology Sydney (Australia), German Aerospace Centre (Germany), and the Shandong Academy of Sciences (China)
Massey University
Researchers at Massey University are working in data processing, speech processing, image/video processing, natural language processing, AI-assisted code generation, geographic information, geospatial knowledge representation and reasoning, location-based systems. They have a wide international collaboration network, which includes Carnegie Mellon University (USA), University of Technology Sydney (Australia), Adelaide University (Australia), Peking University (China), Tsinghua University (China), Wuhan University (China), Polytechnique Montréal (Canada), Wageningen University and Research (Netherlands), National University of Singapore (Singapore), Dublin City University (Ireland), Leeds University (UK), Cardiff University (UK), Ordnance Survey (UK), University of Nottingham (UK), RMIT(Australia), University of Melbourne (Australia), University of Maine (USA) and VNIT Nagpur (India).
Lincoln University
Lincoln University has over 30 years of experience in innovations in AI and applications in a range of domains including agriculture, horticulture, biology and life sciences, ecology and biosecurity environment, water resources, energy and social sciences. For over 15 years, Lincoln has been running the AI centred Complex Systems, Big Data and Informatics Initiative (CSBII) to address complex issues in the above domains using holistic systems approaches based on AI, ML and data modelling to offset fragmented perspectives that have dominated in the past. Researchers at Lincoln University are working in agent and multi-agent applications in agriculture and environment; use of ML to identify emotion and sentiment from social media text; soft computing (neural networks, fuzzy systems and ML); and network and data modelling in complex systems to address seemingly intractable problems encountered in the above domains. Lincoln researchers collaborate internationally with many universities on AI and ML projects, including Universiti Malaysia Sabah (Malaysia), University of Oxford (UK) on mathematical and computational Biology, the Wyss Institute at Harvard University (USA) and Tufts University (USA) on AI to develop conceptual and computational frameworks for development and regeneration in biology, and University of Georgia (USA) (robotics, AI, big data modelling and machine vision in intelligent Agriculture), UNESCO (AI/NN in water resources modelling and expert AI advisor for UNESO); DeLaval Inc. (USA)- one of the largest dairy robot manufacturers in the world (Deep learning for advanced mastitis detection by milking robots); University of Saskatchewan, Canada (holistic system thinking and philosophy in AI and fuzzy cognitive map based modelling of complex socio-ecological and environmental systems for sustainable development and risk mitigation); Peking University (China) (AI and mathematical modelling of disease development in biology), Sun Yat-sen University (China) (Deep Learning and genomic data modelling in health).
Victoria University of Wellington
Researchers at Victoria University of Wellington (VUW) have been working on fundamental research in a range of areas of AI, ML and data science, and playing an international leadership role in evolutionary learning and optimisation, feature selection and big dimensionality reduction, automated deep learning and image analysis, multi-agent systems, categorical and ordinal data analysis, hyperheuristic and learning approaches to planning and scheduling, audio/language and signal processing, explainable AI, stream data mining, generative AI, and autonomous agents and multiagent systems. VUW researchers have been collaborating with other universities and CRIs and successfully applying AI and ML techniques to solve application tasks in primary industry, climate change, biological and health-related areas, high-value/ high-tech manufacturing such as cybersecurity and renewable energy, and ethical/cultural AI and public policies as well as starting a pipeline of training Māori researchers in AI and data science. VUW AI researchers have collaborations with many international organisations, including universities in the USA (e.g. MIT, Michigan State University, Oklahoma State University and University of Rhode Island), China (e.g. Tsinghua University, Nanjing University, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Beijing Jiaotong University, Southern China University, Southern University of Science and Technology, Ocean University of China, and Zhengzhou University), the UK (e.g. University of Warwick, Edinburgh Napier University, University of Surrey and University of Birmingham), Australia (e.g. University of Melbourne, RMIT University, UTS, Central Queensland University and UNSW Canberra, Singapore (e.g. NUS and NTU), and Europe (e.g. Delft University of Technology, Netherlands, and University of Parma, Italy, Technische Universität Wien, Austria, University of Lisbon, Portugal, ZHAW Zurich University of Applied Sciences, Switzerland,). In addition, VUW AI researchers have been collaborating with major international AI communities and societies (e.g. IEEE Computational Intelligence, Computer, and Signal Processing Societies, ACM SigEVO, ACM SigKDD, IJCAI and AAAI), chairing technical committees, and working with globally innovative companies such as IBM, Microsoft, Google, Huawei, KPMG, Xero and Weta Digital. In June 2023, VUW established the Centre for Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, launched by the Minister of Research, Science, and Innovation Dr Ayesha Verrall of the NZ Government and the President of IEEE Computational Intelligence Society.
University of Canterbury
Researchers at the University of Canterbury have extensive international collaborations through projects with Peking University (China) on Bayesian Demographic Inference; RMIT (Australia) on Constructing Pattern Recognition Trees; Université Laval (Canada) on Deep Reinforcement Learning for Creating Game-Playing Agents; Hong Kong University and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (USA) and University of Montreal (Canada) on AI in Medical Imaging; University of Leeds (UK) on using AI in Video-Based Learning (VBL) culminating in the AVW-Space (online platform for VBM); University of Pittsburgh (USA) and University of Illinois (USA) and University of Pennsylvania (USA) and University of Sussex (USA) and University of Malaga (Spain) on collaboration on AI in Education; University of Milan (Italy), Urbana-Champaign (USA) and Missouri (USA), Orsay (France), ANU (Australia), Kiel (Germany), University of Cambridge (UK) on Neuromorphic Computing; Boston University (USA), Turing Centre at Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule in ETH Zürich (Switzerland), University of Queensland (Australia), University of Oxford (UK), Renmin University (China), Copenhagen University (Denmark), Georgetown University (USA), Mangalam University (India) on the philosophy of AI; Leibniz Universität Hannover (Germany), ETH Zürich (Switzerland) on deep learning for autonomous robots and pose tracking; Monash University (Australia) and ANSTO on medical imaging and AI machine learning; CSIRO (Australia), University of Melbourne (Australia), University of Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), Novitom (France), Max Planck Institute (Germany), Technical University of Munich (Germany), Norwegian University of Science and Technology (Norway), Digital Democracy Institute - Simon Fraser University (Canada), University of Montreal (Canada), American Mathematical Society on AI models for drivers of segregation.
University of Waikato
The University of Waikato’s main research expertise is in AI, as seen in Google Scholar [31]. The University has created some of the world’s most popular open source tools such as Weka, Moa and Adams. Weka has more than 10 million downloads and has been cited in more than 20,000 research and applied publications. In 2021, the University launched Te Ipu o te Mahara Artificial Intelligence Institute, which is focused on real-time analytics for big data, machine learning, generative AI, green AI, environmental data science and deep learning. The Institute has a strong international research network, with associate members from Institut Polytechnique de Paris (France), Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (Spain), Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (Belgium), University of Málaga (Spain), TECNALIA (Spain), Basque Research & Technology Alliance (Spain), University of Porto (Portugal), Federal University of Paraná (Brazil), Carnegie Mellon University (USA), University of Texas (USA), Blekinge Institute of Technology (Sweden), Eindhoven University of Technology (Netherlands), University of Sao Paulo (Brazil), Cardiff University (UK), Dalhousie University (Canada), Politecnico di Milano (Italy), Warsaw University of Technology (Poland), University of Münster (Germany), Université Paris-Saclay (France), University of Helsinki (Finland), University of Chile (Chile), Telefonica Research (Spain), INRAE UMR Tetis (France), Universitat de Girona (Spain), Honda Research Institute Europe (Germany), Ekkono Solutions (Sweden), ISI Foundation (Italy), Amazon Web Services (UK), and Shopify (Canada).
University of Auckland
Researchers at the University of Auckland specialise in multi-agent systems, game theory, social network analysis, heuristic search, automated problem solving, ML, computational sustainability, cheminformatics, spatio-temporal data mining, adversarial learning, data stream mining, multi-label classification, natural language processing, natural language understanding, machine reasoning, knowledge representation, deep learning, computer vision and image processing, speech processing, and robotics. The fundamental AI research is applied in areas like agriculture, horticulture, construction, smart cities, healthcare, environmental science, sustainability and renewable energy, and cybersecurity. The university is also home to the Centre of Machine Learning for Social Good, NAOInstitute (the Natural, Artificial, and Organisation Intelligence Institute), and the Machine Learning Group. The School of Computer Science has a flagship project for Ethical Computing and research expertise in Māori Data and Algorithmic Sovereignty (MDSov / MASov). Researchers have extensive international collaborations through projects with Beijing Institute of Technology (China), Beihang University (China), Southwest University (China), Chinese Hong Kong University (China), Harbin Institute of Technology (China), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (China), University of Tasmania (Australia), National University of Singapore, Nanyang Technological University (Singapore), Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (Spain), RIKEN Institute (Japan), University of California at Santa Cruz (USA), Aalborg University (Denmark), Royal Holloway University of London (UK), University of Alberta (Canada), Institute for Study of Learning and Expertise (USA), Carnegie Mellon University (USA), Josef Stefan Institute (Slovenia), Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (Germany), TU Munchen (Germany), Monash University (Australia), RMIT (Australia) and IBM Research.
Among many of these fundamental AI research areas and key applications, Aotearoa New Zealand has been playing an important leadership role in the world in at least the following aspects:
- ML tools such as Weka and R
- Evolutionary learning and optimisation
- Data stream learning/mining
- Image and vision computing applications to primary industry
- Automated design of deep neural network architectures and other deep models
- Feature selection/construction and dimensionality reduction
- Dynamic scheduling and combinatorial optimisation
- Indigenous data sovereignty
- Oversight of government uses of AI and algorithms
- Oversight of harmful content on social media
Examples of fundamental research areas
Symbolic AI

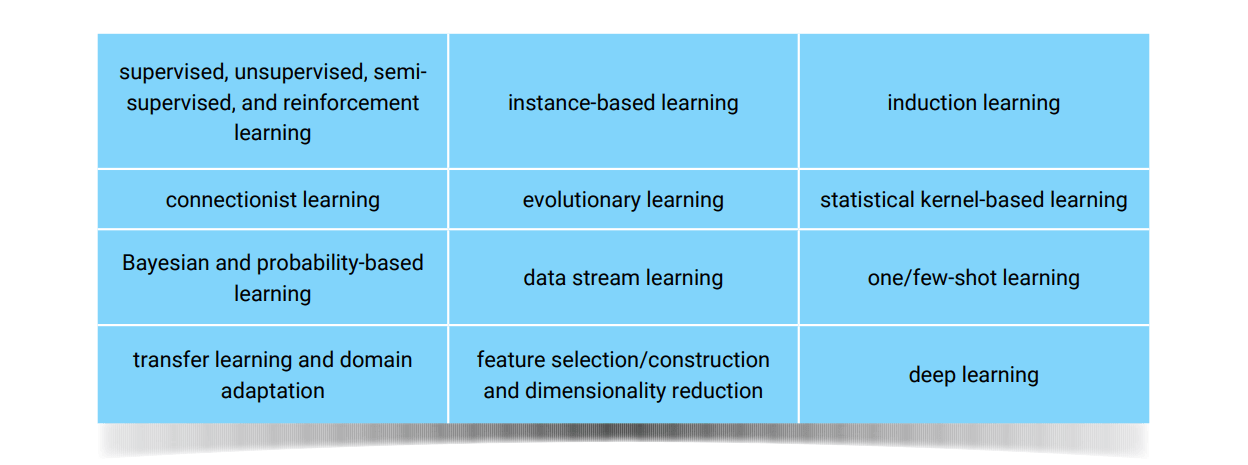
Subsymbolic AI (mainly machine learning)
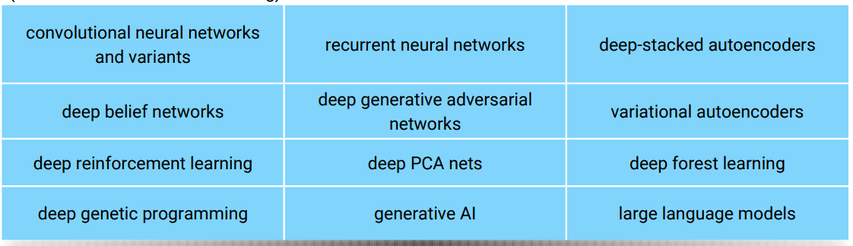
Deep learning (a subdomain of machine learning)
Applications
Applications have been focused on primary industry such as agriculture, aquaculture and open ocean/blue economy, environmental/earth science, geology and disaster management, chemical and material science and engineering, biological and biomedical sciences, as well as marine biology and genomics, public health and medicine, neural science/psychology and drug discovery, cybersecurity, biosecurity, food and water resources, networking and the Internet of Things (IoT), tourism and knowledge travel, sustainable and renewable energy, finance and economics including GDP and CPI prediction, tax, banking, and insurance, and linguistics and languages including natural language processing of te reo Māori.